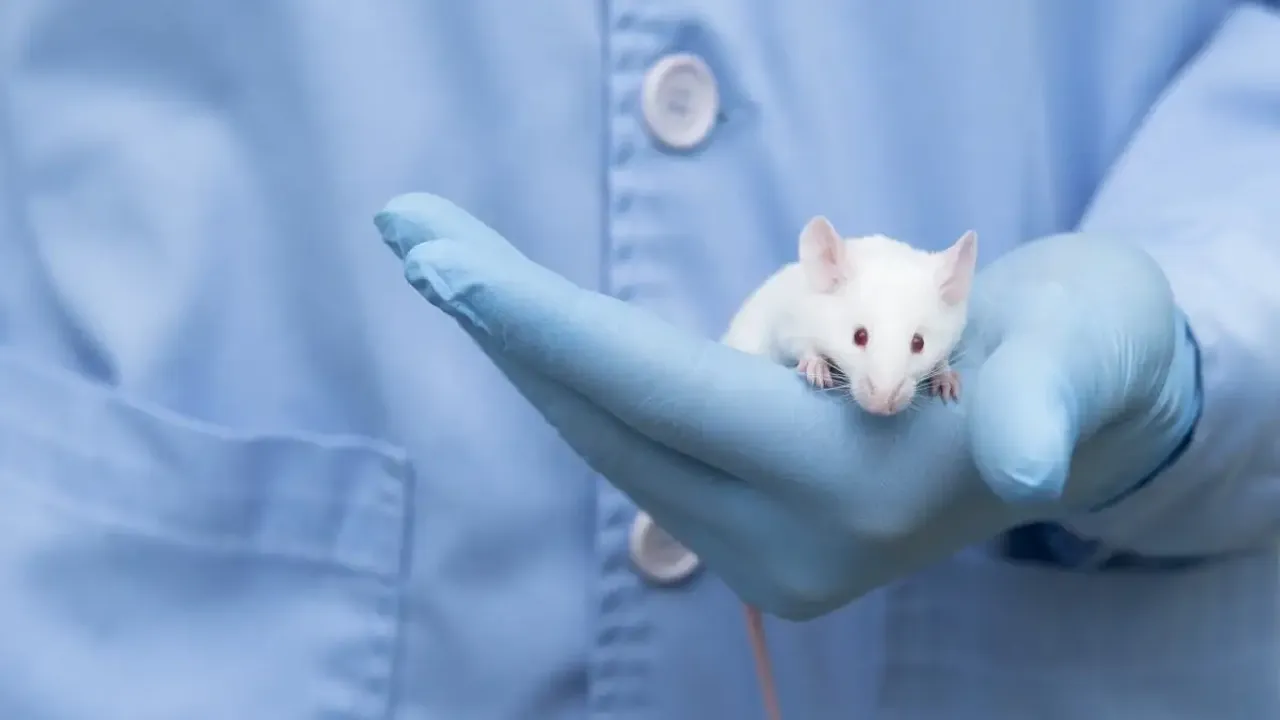
Researchers hope that this technology will allow them to more clearly observe the internal structure of a living organism in its functional state.
“This technology could make blood collection easier by allowing vessels to be seen more clearly, make laser tattoo removal simpler, or help in the early detection and treatment of cancers,” said Stanford University scientist Guosong Hong.
The method used in the research is based on preventing the scattering of light at a specific wavelength in areas of tissue with different refractive indices.
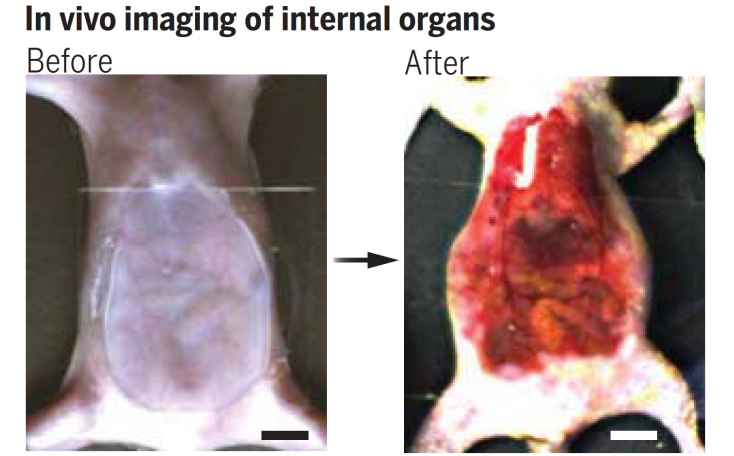 Normally, tissue and surrounding fluids scatter light because they have different refractive indices and transparency is lost. However, if the refractive indices are equalized, light can reflect and pass through deep tissues, resulting in a clearer image.
Normally, tissue and surrounding fluids scatter light because they have different refractive indices and transparency is lost. However, if the refractive indices are equalized, light can reflect and pass through deep tissues, resulting in a clearer image.
It can be a cheap and effective method
To realize this method, the researchers used a food coloring called tartrazine. By absorbing light of certain wavelengths, tartrazine changed the refractive index of the surrounding liquid, significantly reducing the scattering of light.
“This dye is biocompatible, meaning it is safe for living organisms. It is also very cheap and effective; we only need to use a very small amount to make it work.”
When the tartrazine dye was applied to the skin of mice, muscle movements in blood vessels, organs and even the digestive tract could be observed.
A few minutes after the dye is applied, the skin becomes transparent and is washed away after the procedure. The dye that penetrates deeper parts of the body is excreted through urine.
Given that human skin is 10 times thicker than mouse skin, it is not yet clear whether this method will work on humans. The researchers plan to investigate this further.
This study was published in the journal Science.