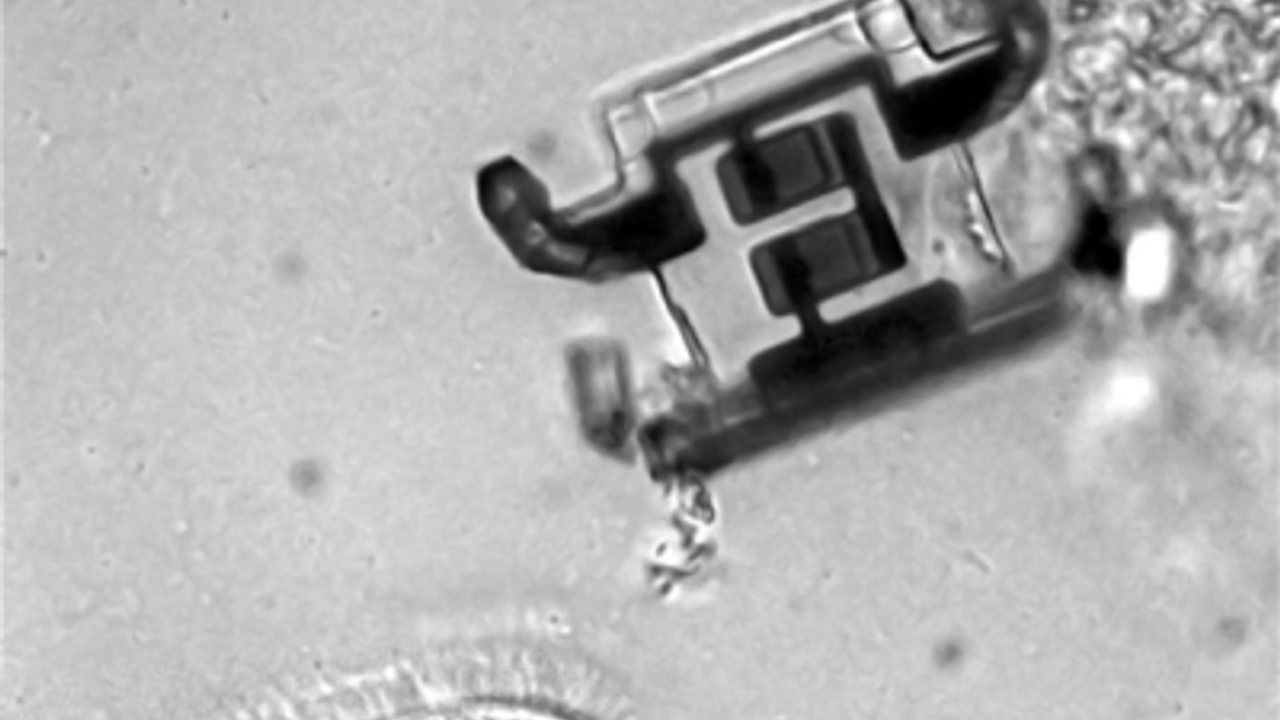
These tiny robots, often referred to as "microbots," are engineered with precision and can perform a variety of functions once inside the body. Designed to be small enough to navigate the bloodstream and other internal systems, these robots can be guided to specific locations to carry out tasks such as targeted drug delivery, internal imaging, and even surgical procedures. Their small size allows them to travel through veins and arteries, potentially reaching areas that are difficult or impossible to access with traditional medical instruments.
The development of these microbots involves advanced materials and sophisticated engineering techniques. Each robot is constructed from biocompatible materials to ensure they do not cause adverse reactions within the body. They are equipped with tiny sensors and actuators that allow them to perform precise movements and interact with their environment. For example, some models are designed to release medication in response to specific biochemical signals, providing a highly targeted approach to treatment.
One of the most promising applications of these microbots is in the realm of personalized medicine. By delivering drugs directly to the affected areas, the robots could significantly increase the efficacy of treatments while minimizing side effects. Additionally, their ability to perform internal diagnostics could lead to earlier detection of diseases and conditions, improving overall patient outcomes.
While the technology is still in the experimental stages, early results are promising. Researchers have demonstrated the feasibility of these microbots in laboratory settings, and ongoing studies aim to further refine their capabilities and assess their safety and effectiveness in clinical environments. The potential impact of this technology on the future of medical treatments is immense, offering a glimpse into a future where minimally invasive procedures and highly targeted therapies become the norm.
As development continues, scientists and engineers are also focusing on overcoming various challenges, such as ensuring the robots can operate reliably within the complex environment of the human body and addressing any potential long-term effects. However, the progress made so far suggests that these microscopic marvels could soon become a vital tool in modern medicine, opening new avenues for treating a wide range of medical conditions with unprecedented precision.